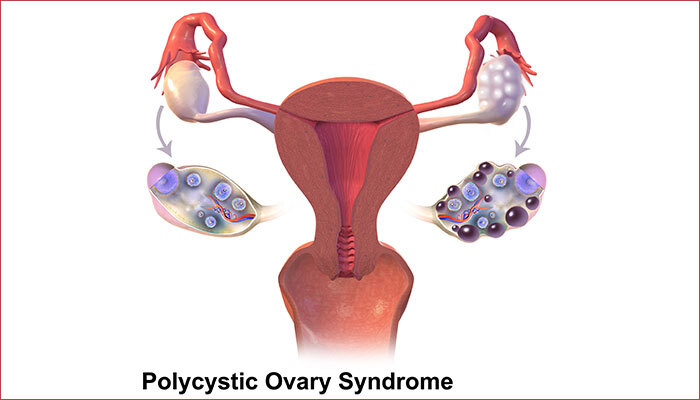
Polycystic (pah-lee-SIS-tik) ovarian syndrome or disease (PCOS/PCOD) is a relatively common yet overlooked medical condition in women. It impacts both the reproductive system as well as metabolic health and is seen in nearly 1 out of 10 women of childbearing age.
This disease is commonly manifested by abrupt ovulation leading to disturbed menstrual cycles, causing infertility, and results in increased hair growth (Hirsutism) that is quite discomforting for the majority of women.
Causes
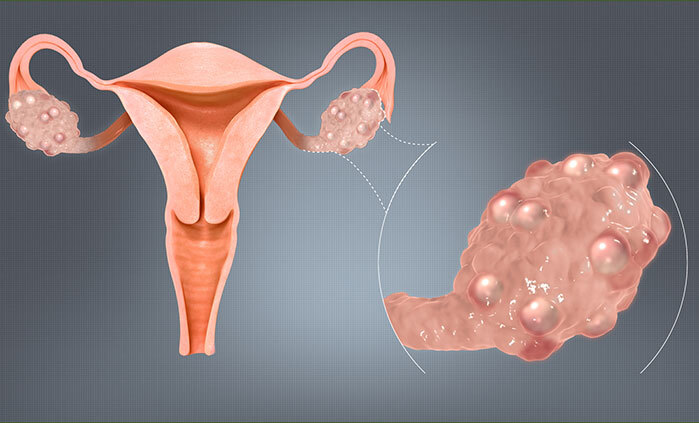
The exact cause of PCOS is unknown. However, among several contributing factors, genetics plays an important role. There are cases reported of maternal history in women. The main underlying cause is hormonal imbalance which can affect ovulation leading to irregular, absent, or heavy menstrual periods.
Though the cause is not yet identified, Genes, insulin resistance, and inflammation are mostly related to PCOS.
Signs and Symptoms

Certain women start experiencing symptoms around the on-set of their first period and interestingly no two women with PCOS have the same exact experience. However, the symptoms are generally more severe in obese (fat) patients. Clinically, the presence of at least two of the following symptoms is indicative of the disease and hence requires treatment.
Below we have mentioned some signs and symptoms of PCOS:
Irregular Periods- Women with PCOS tend to have fewer or 8 periods a year. It happens mainly due to high levels of androgen and too much insulin present in the body.
Heavy Bleeding- When periods are limited they tend to be heavier than the normal ones.
Acne- Increase in the amount of testosterone can make skin oily and cause breakout on several parts of the body including Chest, Face, and Back.
Increased Hair Growth- Hirsutism is yet another symptom of PCOS, Around 70% of women with PCOS experience excess facial and body hair.
Increase in Weight- Though heavyweight and obesity are not the main reason for PCOS, roughly around 70% of suffering women are overweight.
Skin Darkening- Women with PCOS have high levels of hormones and insulin, which can cause the darkening of skin, on the neck, in the groin, and under the breasts.
How PCOS Affects Your Body

Infertility
PCOS restrict women to ovulate on a regular basis, as a result, they don’t produce enough eggs to be fertilized, thus causing infertility in women.
Metabolic Syndrome
Most numbers of women with PCOS are overweight and obese, both PCOS and obesity can cause high blood pressure, high sugar, Low HDL, and high LDL cholesterol. These factors all together can cause Metabolic syndrome, which further makes you prone to heart diseases, stroke, and diabetes.
Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a potentially risky sleep disorder, in which breathing starts and stops while sleeping at night. This disorder is mainly seen in overweight or obese women, moreover, if the woman has PCOS along with obesity, chances of getting sleep apnea become 4-5 times higher.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial Cancer is a type of cancer generally forms on the cells layer that forms the lining of the uterus. It is sometimes referred to as uterine cancer. Women with PCOS are at higher risk since they don’t ovulate on a regular period, the lining won’t shred and keep building up.
Pregnancy and PCOS

PCOS is responsible for irregular periods and makes it hard to be pregnant. It’s been observed that most women with PCOS face fertility issues, this condition can further lead to pregnancy complications.
Women with PCOS are at almost double the risk to deliver a baby prematurely. Also, they are higher risks of miscarriage, blood pressure issue, gestational diabetes. However, there are fertility treatments available to improve ovulation.
Moreover, lowering weight and controlling blood sugar can improve your chances of getting pregnant effectively.
What Lifestyle Modifications Could be Beneficial?

Typical Treatment starts with a change in lifestyle by improving weight, diet, and exercise. Losing even 5-10 % of your body weight can improve the regulation of the menstruation cycle. Losing weight also keeps check on cholesterol levels, insulin levels, and reduces the risk of heart diseases and diabetes.
Studies have proved that food with low carbohydrates is effective to reduce weight and maintain insulin levels. Also, low glycemic index diet that acquires carbohydrates from fruits, veggies, and whole grains helps to maintain the menstrual cycle.